Topics
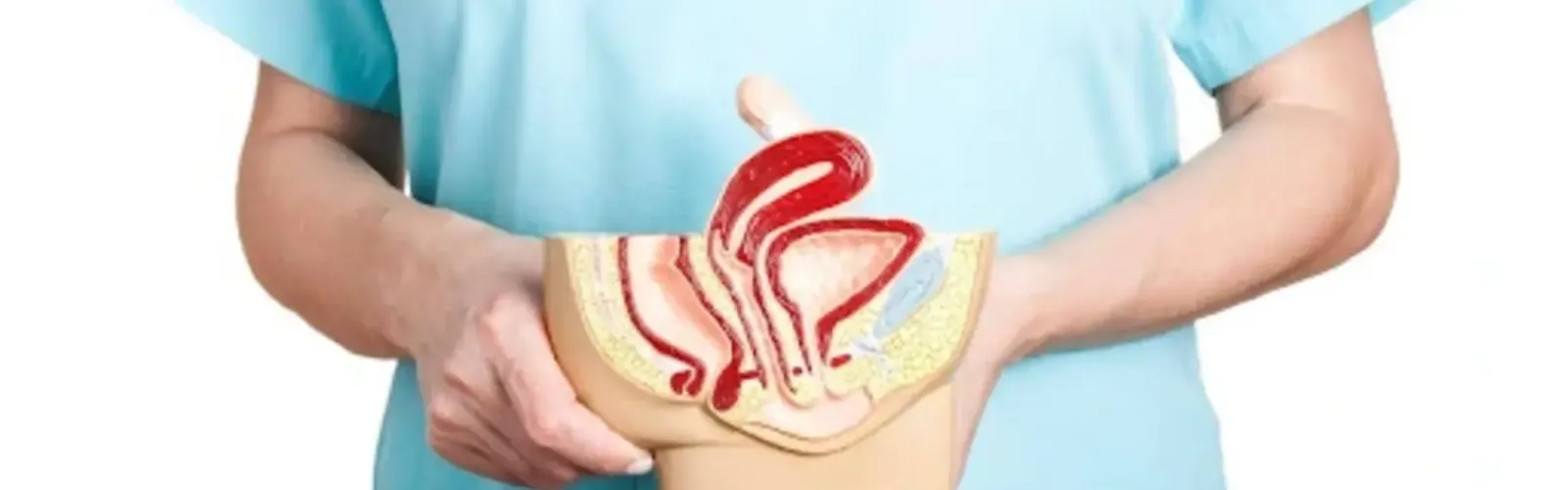
Parts of the Female Reproductive Organs X-Ray Examination of Female Reproductive Organs Conclusion ReferencesAn effective way to understand the organs and health conditions of the female reproductive system is through a picture of female reproductive organs. What are the parts that appear in the picture of the female reproductive system?
The female reproductive organs play a crucial role in the human reproductive system. These organs are responsible for egg production, fertilization, pregnancy, and childbirth. A method to monitor the health of the reproductive organs is through an Ultrasound, which produces a picture of the female reproductive organs and assists in diagnosing health conditions related to them. To learn more about the components of the female reproductive system, continue reading this article.
Parts of the Female Reproductive Organs
In general, the female reproductive organs are divided into two main categories: external and internal reproductive organs. When an Ultrasound is performed, it produces a picture of the female reproductive organs, showing some of these components. So, what are the parts of the reproductive system? Here is an explanation of each organ in the female reproductive system.
1. External Reproductive Organs
The external reproductive organs of women consist of parts located outside the body, which play a role in protection and sexual stimulation. The term vulva refers to the entire external part of the female reproductive system. The vulva protects internal organs from infection and injury, and it plays a role in sexual activity. The vulva consists of several key parts:
- Labia Majora:
The outer folds of skin that are thick and contain fatty tissue and sweat glands. They help protect the internal parts of the vulva from friction and infection.
- Labia Minora:
The smaller, thinner inner folds of skin. The labia minora contain numerous blood vessels and nerve endings, making them very sensitive to stimulation.
- Clitoris:
A small, round organ located at the top of the vulva. It contains thousands of nerve endings, making it highly sensitive and an important part of sexual stimulation.
- Vestibule:
The area inside the labia minora that includes the urethra (the opening where urine exits) and the vaginal opening.
- Bartholin's Glands:
Small glands located on either side of the vaginal opening that produce fluid to lubricate the vagina during sexual intercourse.
- Mons Pubis:
A fatty area located above the labia majora, covered by pubic hair after puberty. The mons pubis helps protect the pubic bone from pressure and friction.
2. Internal Reproductive Organs
Next, in a picture of female reproductive organs, the internal reproductive organs are shown. These organs are involved in ovulation, fertilization, and pregnancy. They are located deeper within the body. Here are the main internal organs in the female reproductive system:
- Vagina:
The vagina is a tubular structure that connects the external organs to the uterus. Its main functions include serving as a passage for sperm during intercourse, allowing menstrual blood to exit the body, and serving as the birth canal during labor. The vagina has elastic walls that can expand during sexual activity and childbirth, and it has protective mechanisms, such as an acidic pH to prevent harmful bacterial growth.
- Uterus (Womb):
The uterus is a pear-shaped organ where a fertilized egg develops into a fetus. It consists of three main layers: the endometrium (the inner lining that sheds during menstruation and where an embryo implants), the myometrium (a thick muscular layer that helps expel the baby during labor), and the perimetrium (the outer layer that protects the uterus). The uterus is also involved in regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the body for pregnancy.
- Fallopian Tubes:
The fallopian tubes are the channels that connect the ovaries to the uterus. Their main role is to transport the egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization typically occurs within the fallopian tubes if sperm meets the egg. If fertilization happens, the resulting embryo travels to the uterus for implantation.
- Ovaries (Ovarian Follicles):
The ovaries are oval-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They are responsible for producing eggs (ova) and releasing them during ovulation. The ovaries also produce reproductive hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Each ovary contains thousands of follicles, which contain immature eggs. Throughout a woman’s reproductive years, only a few of these follicles will mature and release an egg each month.
X-Ray Examination of Female Reproductive Organs
Ultrasound examinations are frequently used in the medical field to create images of the female reproductive organs and diagnose various conditions related to the reproductive system. Some specific radiological procedures are employed to evaluate the health of organs such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Here are some key functions of radiological procedures in assessing the health of female reproductive organs:
1. Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is an radiological procedure that uses a contrast dye to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes. This procedure is often performed to diagnose infertility issues, especially if there are blockages in the fallopian tubes. HSG can also detect structural abnormalities such as septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, polyps, or fibroids. This test can also evaluate post-surgical conditions of the uterus or fallopian tubes and ensure that the fallopian tubes are open after procedures like tubal ligation.
2. Detection of Uterine Abnormalities
Ultrasound, either trans abdomen or trans vaginal, can help detect various uterine abnormalities, such as uterine fibroids, endometrial polyps, adenomyosis, and congenital anomalies. For instance, fibroids are benign tumors that grow inside or around the uterine walls, which can cause pain, heavy bleeding, or difficulty in conceiving. Endometrial polyps are abnormal growths in the uterus that can lead to abnormal bleeding or fertility problems. Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue lining the uterus grows into the muscle wall of the uterus, causing painful periods and heavy bleeding. Women may also have congenital uterine abnormalities that can impact pregnancy and increase the risk of miscarriage.
3. Diagnosing Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the inner lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, such as in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs. While Ultrasounds is not the primary method for diagnosing endometriosis, they can be used in some cases to assess structural changes in the pelvic organs due to adhesions or to detect endometriosis-related cysts.
4. Ovarian Tumors or Cysts
Ultrasound can assist in detecting abnormal masses in the ovaries, although CT scans are typically more effective. Conditions such as ovarian cysts, tumors, or ovarian torsion can sometimes be identified by Ultrasound images, especially if the masses are large enough to cause noticeable symptoms.
5. Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy
An ultrasound of the female reproductive organs can help assess ectopic pregnancy, a dangerous condition where the embryo grows outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube. This condition requires immediate medical attention. Trans abdominal ultrasound can also help detect internal bleeding or structural changes in the pelvic organs, although a transvaginal ultrasound remains the primary diagnostic tool.
6. Evaluating Trauma or Injury to Reproductive Organs
Trauma to the reproductive organs can occur from accidents, violence, or medical complications. CT scans are useful for assessing damage to the pelvic bones that may affect nearby reproductive organs. Additionally, CT scan with contrast or MRI can be used to detect bleeding or structural changes caused by trauma.
Conclusion
The female reproductive organs consist of both external and internal parts that play vital roles in the reproductive system. Radiological images of the female reproductive organs help monitor and control the health of these organs. It is recommended that women undergo routine examinations of their reproductive organs at medical centers. Hospitals like IHH Healthcare Malaysia offer radiology services to assess female reproductive health, with multiple payment options available for healthcare. Don’t hesitate to get yourself checked at IHH Healthcare Malaysia today!
References
- https://www.iowaradiology.com/visualizing-female-reproductive-anatomy-how-an-hsg-works-2/
- https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/hysterosalp
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometriosis
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ectopic-pregnancy
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/hsg-test/vid-20084751#:~:text=Hysterosalpingography%2C%20or%20HSG%2C%20is%20an,is%20injected%20into%20the%20uterus.